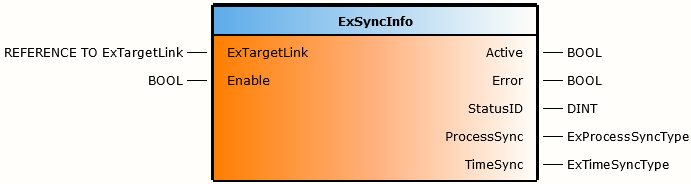
功能块
参数
输入/输出 |
参数 |
数据类型 |
说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
IN |
ExTargetLink |
REFERENCE TO ExTargetLink |
连接至 exOS 目标配置。 |
IN |
Enable |
BOOL |
只要该输入被设置,功能块就处于激活状态。 |
OUT |
Active |
BOOL |
功能块激活。 |
OUT |
Error |
BOOL |
执行过程中发生错误。 |
OUT |
StatusID |
DINT |
状态信息。 |
OUT |
ProcessSync |
ExProcessSyncType |
进程同步信息。 |
OUT |
TimeSync |
ExTimeSyncType |
时间同步信息 |
数据类型
ExProcessSyncType - 进程同步信息。
参数 |
数据类型 |
说明 |
|---|---|---|
Local |
ExProcessSyncTargetType |
本地系统的进程同步信息。 |
Local.CycleTime |
UDINT |
数据报文路由器的周期时间(微秒)。 |
Local.ProcessTime |
UDINT |
数据报文路由器的处理时间(微秒)。 |
Local.IdleTime |
UDINT |
数据报文路由器的空闲时间(微秒)。 |
Local.CycleTimeViolations |
UDINT |
违反周期时间的次数(在 AR 上始终为 0)。 |
Local.MissedCycles |
UDINT |
错过周期的次数(在 AR 上始终为 0)。 |
Remote |
ExProcessSyncTargetType |
远程系统的进程同步信息。 |
Remote.CycleTime |
UDINT |
数据报文路由器的周期时间(微秒)。 |
Remote.ProcessTime |
UDINT |
数据报文路由器的处理时间(微秒)。 |
Remote.IdleTime |
UDINT |
数据报文路由器的空闲时间(微秒)。 |
Remote.CycleTimeViolations |
UDINT |
违反周期时间的次数(在 AR 上始终为 0)。 |
Remote.MissedCycles |
UDINT |
错过的周期数(在 AR 上始终为 0)。 |
ExTimeSyncType - 时间同步信息。
参数 |
数据类型 |
说明 |
|---|---|---|
TargetResponsive |
BOOL |
exOS 目标正在响应(即在超时间隔内响应请求)。 |
PrecisionReached |
BOOL |
exOS 目标已达到配置的同步精度。 |
PrecisionError |
DINT |
当前 Linux 中的 NETTIME 偏差,以微秒为单位。 |
该功能块只需一个参数,即 exOS 目标配置生成的全局配置链接地址(包含目标名称)
ExSyncInfo_0(ExTargetLink := ADR(gTarget_0), Enable := TRUE);
关于 StatusID 输出,请参阅 功能块 StatusID。
该功能块显示数据连接的当前同步状态。
有关同步功能的更多信息,请参阅 " 开发人员"章节 中的"时间同步" 和 "进程同步" 。
该功能块输出两个类别:
•进程同步
在这里, 数据集消息路由器两侧之间的同步 是 可视化的。该服务在 AR 和 Linux 上循环运行,使用 以微秒为单位 的 给定 CycleTime。ProcessTime 显示 DMR 用于处理应用程序之间数据 的 微秒数 ,因此 IdleTime 是下一个循环之前的剩余时间。 (注:这与系统的一般 "闲置时间 "无关。)
如果 ProcessTime 超过 CycleTime, CycleTimeViolations 计数器就会增加。这主要是针对 Linux(远程)目标,因为假定 AR 系统的配置方式不会发生违反周期时间的情况。同样, MissedCycles 计数器 只 适用于 Linux(远程)系统,它显示 Linux 上的 DMR 是否 错过了来自 AR 的周期。 如果 DMR 周期时间 (在 exOS 目标配置中设置)很短, 就 会出现这种 情况, 这通常是非实时 Linux 的调度问题。 如果 Linux 应用程序需要确保进程高度同步 , 也可通过 exos_api使用missed_ar_cycles。
•时间同步
时间同步基本上有两个输出: TargetResponsive 表示 DMR 内部的时间同步机制 已启动并运行,并且 AR 端持续收到回复;而 PrecisionReached则 表示同步机制已达到 exOS 目标配置 中 的给定 精度 。 PrecisionError 是时间同步机制的当前误差,应保持在配置 精度 范围内 。如果 PrecisionError在 较长时间内 超出配置 精度 ,同步机制将把 PrecisionReached 设为 FALSE。对于需要精确时间同步的应用程序, EXOS_DATAMODEL_EVENT_SYNC_STATE_CHANGED 和 in_sync可 通过 exos_api 为 Linux 应用程序 提供此信息 。
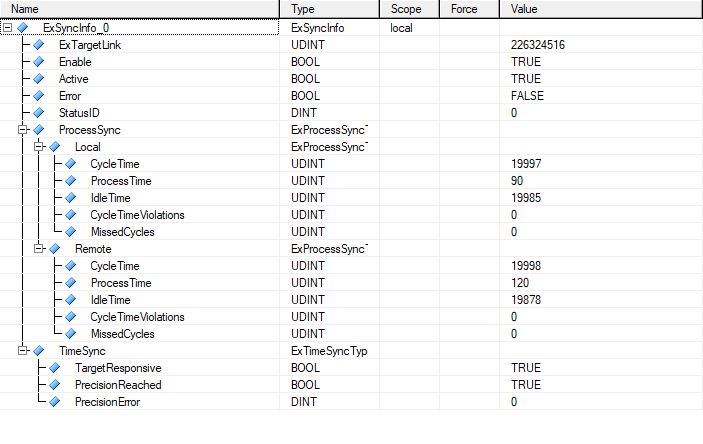
Function Block
Parameters
I/O |
Parameter |
Data type |
Description |
IN |
ExTargetLink |
REFERENCE TO ExTargetLink |
Connection to exOS Target configuration. |
IN |
Enable |
BOOL |
The function block is active as long as this input is set. |
OUT |
Active |
BOOL |
Function block active. |
OUT |
Error |
BOOL |
Error occurred during execution. |
OUT |
StatusID |
DINT |
Status information. |
OUT |
ProcessSync |
ExProcessSyncType |
Process synchronization information. |
OUT |
TimeSync |
ExTimeSyncType |
Time synchronization information. |
Data types
ExProcessSyncType - Process synchronization information.
Parameter |
Data type |
Description |
Local |
ExProcessSyncTargetType |
Process synchronization information for the local system. |
Local.CycleTime |
UDINT |
Cycle time of the Data Message Router in microseconds. |
Local.ProcessTime |
UDINT |
Process time of the Data Message Router in microseconds. |
Local.IdleTime |
UDINT |
Idle time of the Data Message Router in microseconds. |
Local.CycleTimeViolations |
UDINT |
Number of cycle time violations (always 0 on AR). |
Local.MissedCycles |
UDINT |
Number of missed cycles (always 0 on AR). |
Remote |
ExProcessSyncTargetType |
Process synchronization information for the remote system. |
Remote.CycleTime |
UDINT |
Cycle time of the Data Message Router in microseconds. |
Remote.ProcessTime |
UDINT |
Process time of the Data Message Router in microseconds. |
Remote.IdleTime |
UDINT |
Idle time of the Data Message Router in microseconds. |
Remote.CycleTimeViolations |
UDINT |
Number of cycle time violations (always 0 on AR). |
Remote.MissedCycles |
UDINT |
Number of missed cycles (always 0 on AR). |
ExTimeSyncType - Time synchronization information.
Parameter |
Data type |
Description |
TargetResponsive |
BOOL |
The exOS Target is responding (i.e. answering a request within the timeout interval). |
PrecisionReached |
BOOL |
The exOS Target has reached the configured precision of synchronization. |
PrecisionError |
DINT |
Current NETTIME deviation in Linux, measured in microseconds. |
Usage
The function block only takes one parameter, which is the address to the global configuration link generated by the exOS Target configuration (with the name of the target)
ExSyncInfo_0(ExTargetLink := ADR(gTarget_0), Enable := TRUE);
For the StatusID output, please refer to the Function block StatusIDs.
Description
This function block shows the current synchronization state of the data connection.
For more information regarding the synchronization functionality, see the chapters Time Synchronization and Process Synchronization in the developer section.
The function block outputs two categories:
•ProcessSync
Here, the synchronization between the two sides of the Dataset Message Router is visualized. This service runs in a cyclic loop on both Automation Runtime and Linux using the given CycleTime in microseconds. The ProcessTime shows how many microseconds the DMR used for processing data between applications, and thus IdleTime is the remaining time until the next cycle. (Note: This has nothing to do with the general "Idle Time" of the system)
Should the ProcessTime exceed the CycleTime, the CycleTimeViolations counter is increased. This is mainly intended for the Linux (Remote) target, as it is assumed that the Automation Runtime system is configured in a way that no cycle time violation can occur. Similarly, the MissedCycles counter only applies to the Linux (Remote) system, where it shows, whether the DMR on Linux has missed out on a cycle from Automation Runtime. This can happen if the DMR Cycle Time (set in the exOS Target configuration) is very short, which is normally a problem for a non-realtime Linux to schedule. The missed_ar_cycles is also available via the exos_api for Linux applications, should they need to ensure high process synchronization.
•TimeSync
The Time Synchronization basically has two outputs: TargetResponsive means that the time synchronization mechanism inside the DMR is up and running, and replies are continuously received on the Automation Runtime side, whereas the PrecisionReached indicates that the synchronization mechanism has reached the given Precision from the exOS Target configuration. The PrecisionError is the current error of the time synchronization mechanism, which should stay within the configured Precision. Should the PrecisionError be outside the configured Precision during a longer time period, the synchronization mechanism will set PrecisionReached to FALSE. For applications where accurate time synchronization is desired, the EXOS_DATAMODEL_EVENT_SYNC_STATE_CHANGED and in_sync supplies this information via the exos_api for Linux applications.